Tap Macau’s Workforce Without the Complexity: EOR Made Simple
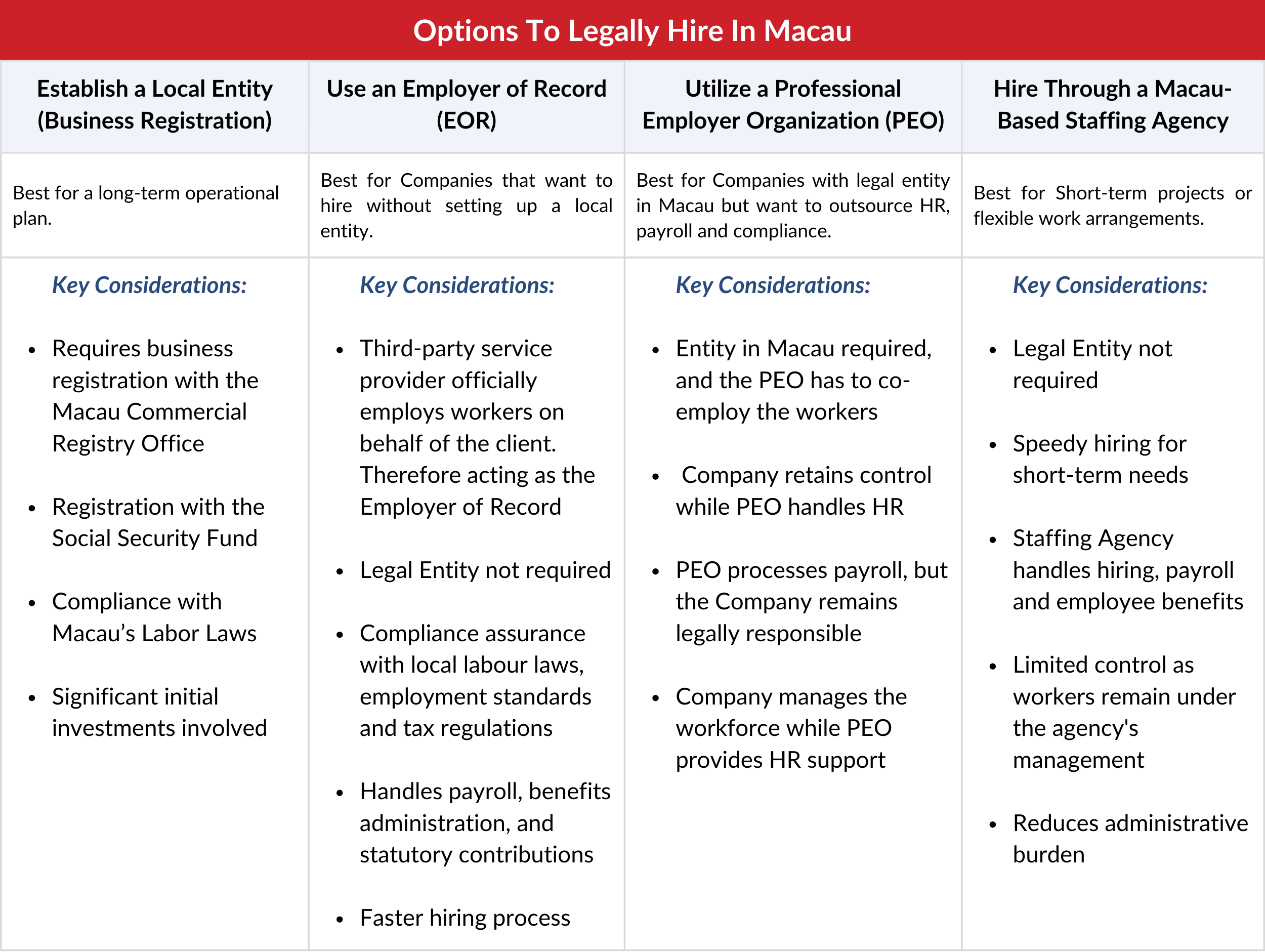
Hiring international talent in Macau offers immense potential, especially for companies looking to expand into Greater China without the regulatory complexities of Mainland China. As a Special Administrative Region (SAR), Macau operates under its own legal and labor framework, making it both a strategic and accessible location for businesses. With a 99.87% literacy rate and a multilingual population, the region offers a skilled and adaptable remote workforce in Macau, particularly across industries like gaming, hospitality, construction, and retail (Source: GlobalData). However, navigating local labor laws, work permits, and compliance obligations can be time-consuming—especially for companies without a physical presence.
That’s where an Employer of Record (EOR) in Macau becomes a game-changer. Instead of undergoing full business incorporation in Macau, companies can use an EOR to legally hire and manage talent, while staying fully compliant with local laws. From handling payroll in Macau to tax contributions and employment contracts, the EOR model streamlines the entire process. If you’re building a remote workforce, testing new markets, or scaling quickly, EOR solutions offer an efficient alternative to traditional recruitment services in Macau, giving you speed, flexibility, and peace of mind.

Hiring in Macau doesn’t have to be complicated.
With the right EOR partner, you get boots on the ground—without getting buried in bureaucracy.